ในยุคอุตสาหกรรม 4.0 เครื่องมือจำพวกโรบอทเชิงกระบวนการและระบบอัตโนมัติอัจฉริยะมีส่วนช่วยสนับสนุนให้ภาคธุรกิจมีประสิทธิภาพนำเสนอสินค้าบริการได้รวดเร็วด้วยต้นทุนที่ต่ำกว่ากิจการทั่วไปในปัจจุบัน กระบวนการหรืองานที่จะได้รับประโยชน์จากเทคโนโลยี RPA (Robotic Process Automation) โดยทั่วไปแล้วจะมีลักษณะเป็นงานที่รูทีนไม่หวือหวาไม่ซับซ้อนแต่เกี่ยวข้องกับซอฟต์แวร์มากกว่าหนี่งตัวขึ้นไป
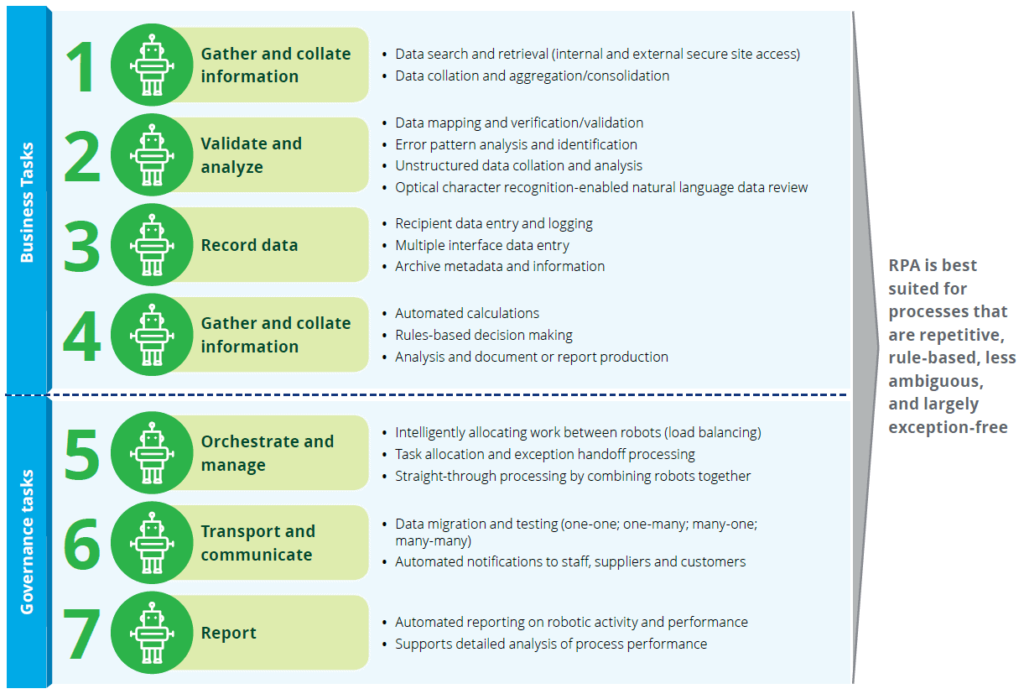
Source: Automation is here to stay, Deloitte
“โรบอท” หรือ ซอฟต์แวร์จากเทคโนโลยี RPA ไม่ได้เป็นเพียงซอฟต์แวร์ที่ออกแบบมาเพื่อตอบสนองการแปลงรูปองค์กรด้วยเทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศเท่านั้น แต่ขีดความสามารถของโรบอทที่กล่าวถึงนี้คือความสามารถในการเลียนแบบการทำงานในกระบวนการต่างๆ ที่เป็นกิจวัตรของผู้ปฏิบัติงาน เช่น การใช้งานหรือการมีปฏิสัมพันธ์ผ่านหน้าจอซอฟต์แวรต่างๆ ซึ่งมีแบบแผนการตัดสินใจง่ายๆ ตัวอย่างของงานประเภทนี้ได้แก่กระบวนการทางธุรกิจหรืองานทั่วไปที่นำข้อมูลที่ได้รับจากแหล่งหรือจากซอฟต์แวร์ตัวหนึ่ง และไปป้อนให้กับซอฟต์แวร์อีกตัวหรือป้อนให้กับซอฟต์แวร์บางตัวที่อยู่คนละระบบ
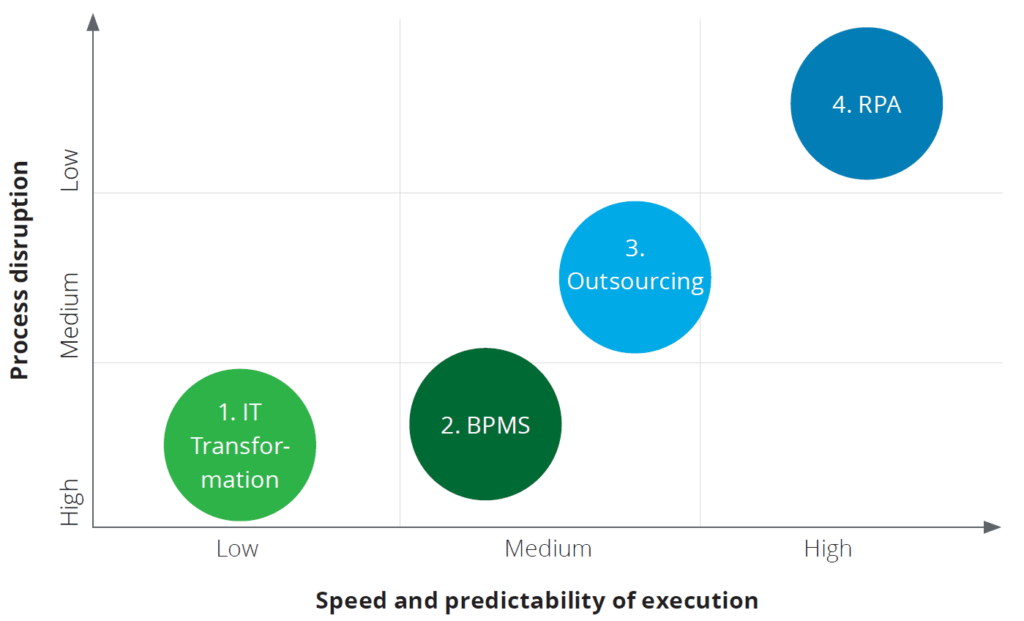
Source: Automate this, Deloitte
ข้อจำกัดในหลายบริษัทคืองานที่มีขนาดใหญ่บางงานถูกทำซ้ำเพียงไม่กี่ครั้งต่อวัน งานเหล่านี้จึงไม่ได้รับประโยชน์จากกระบวนการอัตโนมัติที่สนับสนุนด้วยเทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศ ส่วนการนำระบบอัตโนมัติไกปใช้กับงานที่มีขนาดเล็กเช่นงานที่เกิดขึ้นจากการใช้งานเครื่องคอมพิวเตอร์ส่วนนั้นเกิดประโยชน์ก็จริงแต่ก็จำกัดมากๆ อย่างไรก็ดี เทคโนโลยี RPA ได้คำนึงถึงช่องว่างดังกล่าว คือ ลดความเหลื่อมล้ำระหว่างงานเหล่านั้น ผลการวิจัยของ Deloitte ได้กล่าวไว้ว่านอกเหนือจากการลดต้นทุนการทำงาน ธุรกิจที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี RPA ต่างก็มีประสบการณ์ที่ดีอื่นๆ เช่น การลดวงจรเวลาที่ใช้ทำงานหนึ่ง เพิ่มประสิทธิผล ก่อให้เกิดความยืดหยุ่นในแง่ของการต่อขยายกระบวนการในงานต่างๆ มีความถูกต้องแม่นยำที่มากขึ้น ส่งผลต่อขวัญกำลังใจพนักงาน และได้รายละเอียดข้อมูลการดำเนินการในขั้นตอนต่างๆ อย่างละเอียด
ADJUSTING WORK-WORKER ECOSYSTEM
ผลการสำรวจผู้ปฏิบัติงานในสายงานการบุคคลในบริษัทข้ามชาติโดย Deloitte ชั้ให้เห็นว่าการใช้นำเทคโนโลยี RPA เข้ามาใช้นั้นในที่สุดแล้วจะนำไปสู่ปรากฎการณ์แรงงานดิจิทัล (Digital Workforce) อันเปี่ยมไปด้วยสมรรถภาพไร้การเปรียบเทียบไม่ว่าจะเป็นการทำงานในกระบวนการใดก็ตาม การนำเอา RPA มาใช้งานจริงไม่ว่าจะในองค์กรธุรกิจใดก็ตาม จำเป็นต้องมีปรับเปลี่ยนหรือแม้กระทั่งออกแบบโครงสร้างองค์กรใหม่ ซึ่งอาจจะต้องโยกย้ายเปลี่ยนกลุ่มกระบวนการ หรือแม้แต่เปลี่ยนโครงสร้างรวมทั้งขอบเขตความรับผิดชอบในระดับแผนกหรือระดับกลุ่ม
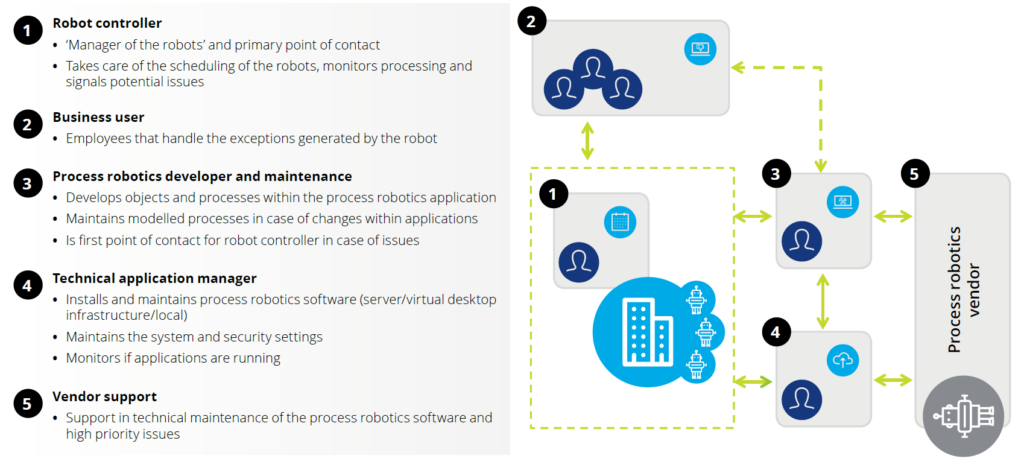
Source: Automation is here to stay, Deloitte
ในขณะที่มีการเปลี่ยนแปลงครั้งใหญ่หรือแม้กระทั่งสูญพันธ์ในบางงานหรือในบางบทบาทหน้าที่ พบว่าก็จะมีงานหรือบทบาทหน้าที่ใหม่เกิดขึ้นเสมอ ตัวอย่างเช่น หน้าที่หรืองานที่เรียกว่า “โรบอทควบคุม” ที่ทำหน้าที่จัดการตารางงานและคอยตรวจตรากระบวนการที่ประกอบอยู่ในงานหนึ่งๆ นักพัฒนา “โรบอท” ที่ต้องปรับแบบจำลองกระบวนการเมื่อรูปแบบงานหรือลักษณะทางกระบวนของงานเกิดความเปลี่ยนแปลง นักพัฒนาโรบอทยังต้องทำหน้าที่เป็นหน่วยเฝ้าระวังด่านหน้าเพื่อจัดการกับปัญหาที่อาจเกิดขึ้นกับ RPA โรบอทได้ทันท่วงที
โรงงานอัจฉริยะหรือ Smart Factory คือระบบงานที่มีความยืดหยุ่น ปรับปรุงและปรับแต่งตัวเอง เรียนรู้และเติบโตจากเหตุการณ์ต่างๆ ที่เกิดด้วยความเร็วในระดับเวลาจริงหรือเกือบจะเวลาจริง ปฏิบัติงานได้ด้วยตัวเองไม่ว่าไม่ว่าจะเป็นในหน้าที่ตำแหน่งงานใดก็ตาม อย่างไรก็ดีผลลัพธ์และคุณประโยชน์ที่จะได้รับจากการนำเอาแนวคิด Smart Factory ไปใช้ย่อมแตกต่างออกไปตามธรรมชาติของกระบวนการทำงานในธุรกิจนั้นๆ
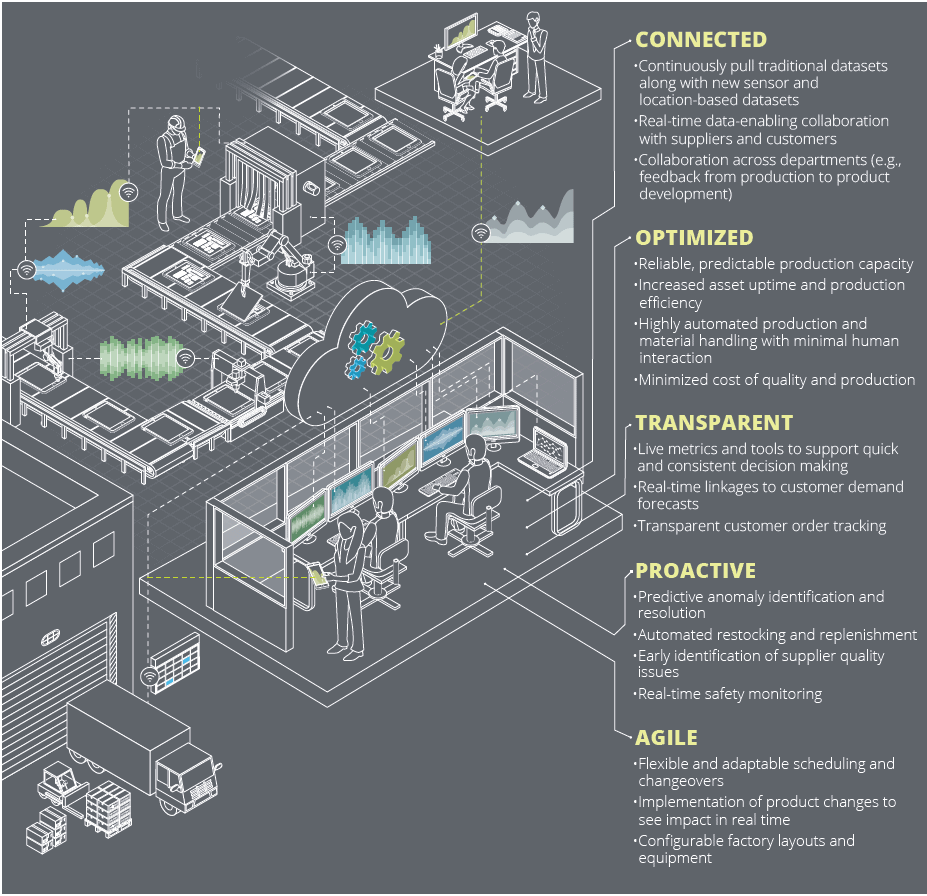
Source: Automation is here to stay, Deloitte
Deloitte ได้จำแนกเทคโนโลยีที่อำนวยความสะดวกสนับสนุนการไหลของข้อมูลระหว่างหน้างานและการประมวลผลในโลกดิจิทัล เทคโนโลยีเหล่านี้ขับเคลื่อนโครงข่ายอุปทานแบบดิจิทัลและนำไปสู่การเป็น Smart Factory ที่มีขีดความสามารถอันทรงพลังที่สามารถสร้างโอกาสที่มาพร้อมกับกระบวนการผลิตแบบดิจิทัล ผู้ประกอบการต้องตระหนักถึงความสำคัญในการวางรากฐานเชิงดิจิทัลที่จะเกิดขึ้นกับองค์กรกับเม็ดเงินที่ลงทุนไปกับเทคโนโลยี Smart Factory
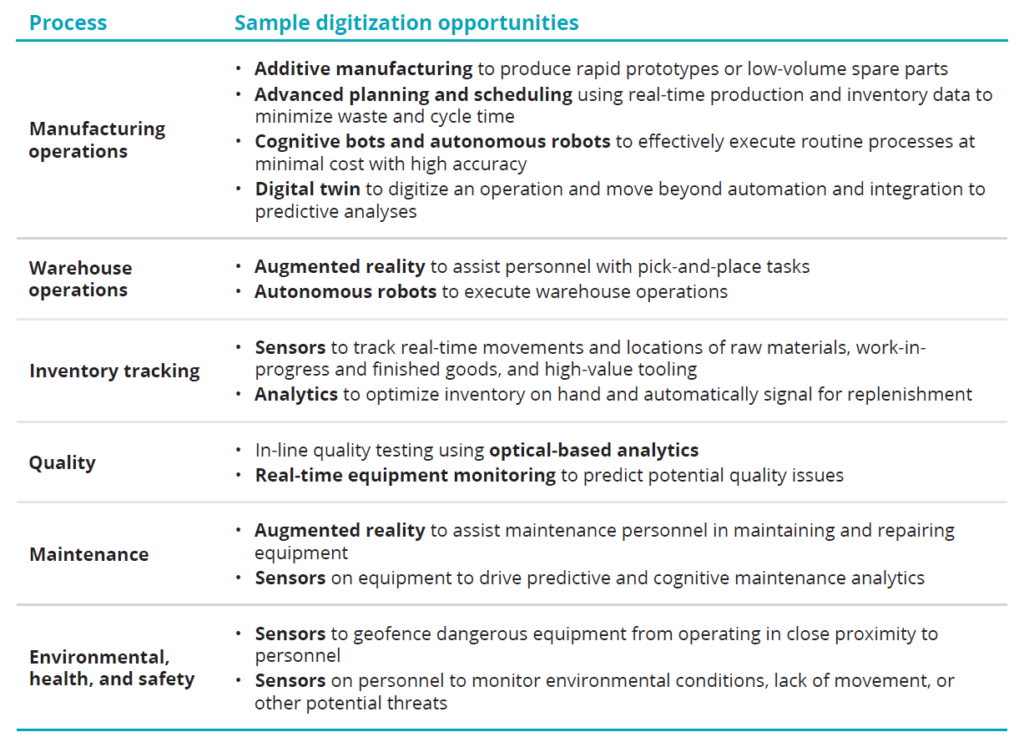
Source: Deloitte Analysis, Deloitte University
การลงทุนในเทคโนโลยี Smart Factory ในทางปฏิบัติแล้วมักเริ่มต้นด้วยการตั้งวัตถุประสงค์ที่ชัดเจนและเฉพาะเจาะจง จากนั้นสิ่งที่ตามมาคือแนวทางของการแปรรูปทางดิจิทัลที่สามารถขับเคลื่อนและสร้างคุณค่ารูปแบบใหม่ให้กับองค์กร อย่างไรก็ดีการสร้างและยกระดับ Smart Factory ไม่ได้ยากหรือมีแนวทางที่เป็นอุปสรรคจนทำไม่ได้ และเพื่อที่จะให้เป็น Smart Factory ที่แท้จริงผู้ประกอบการจำเป็นต้องหาจุดเริ่มต้นให้ได้สักจุดหนึ่งก่อน แนวทางปฏิบัติที่ประสบความสำเร็จมักเริ่มต้นจากจุดเล็กๆ ก่อนเสมอ ทดสอบคอนเซ็ปต์ภายใต้สภาวะที่ควบคุมได้ จากนั้นจึงเริ่มขยายผลลัพธ์โดยนำบทเรียนที่ได้จากการทดสอบมาขยายผลการทดสอบที่มีความครอบคลุมมากกว่าเดิม เมื่อประสบผลสำเร็จในขั้นตอนนี้แล้ว จึงค่อยขยายไปยังกระบวนการต่างๆ ให้กว้างขึ้นสู่สายการผลิตอื่นจนครอบคลุมไปทั้งโรงงานประกอบการ หากเป็นดั่งเช่นนี้แล้วโอกาสในการสร้างสรรค์คุณค่าให้แก่องค์กรจะเติบโตเป็นทวีคูณ
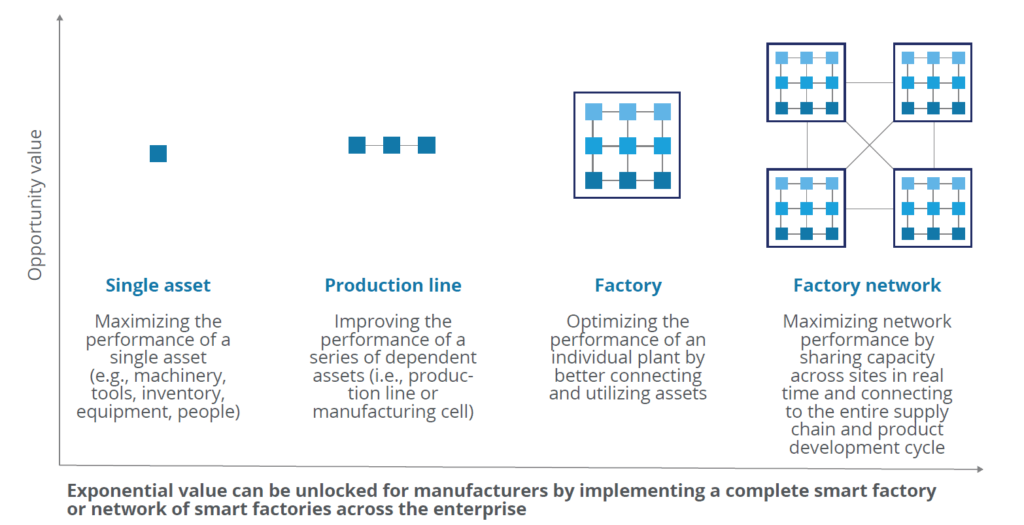
Source: Deloitte Analysis, Deloitte University
กิจการใดก็ตามที่ละเลยเทคโนโลยี RPA หรือเทคโนโลยีอัตโนมัติอื่นๆ ย่อมพลาดโอกาสครั้งสำคัญ เช่น การเข้าถึงประสิทธิภาพและคุณภาพในส่วนที่องค์กรยังเข้าไม่ถึง การบรรเทาความเสี่ยง นวัตกรรม รวมถึงการเติบโตขององค์กร เพียงแค่การยอมรับหลักการเทคโนโลยี PRA ก็สามารถสร้างความเปลี่ยนแปลงให้กับธุรกิจอย่างลึกซึ้งอันเนื่องมาจากการทบทวนโครงสร้างของและวิศวกรรมทางองค์กร ด้วยเหตุนี้ การอบรม การให้การศึกษา รวมทั้งการฝึกฝนทักษะใหม่จึงเป็นภาระกิจสำคัญที่จะทำให้การเปลี่ยนแปลงนี้เป็นไปได้และประสบความสำเร็จ













