Article by: Suwan Juntiwasarakij, Ph.D., MEGA Tech Senior Editor
ปฏิเสธไม่ได้ว่าระบบออโตเมชันมีส่วนในการปฏิวัติการประกอบธุรกิจมาโดยตลอด นับตั้งแต่กระบวนการจัดการหน้าร้านไปจนถึงการจัดการหลังร้าน ตัวอย่างที่เห็นได้ชัด เช่น การชอปปิ้งโดยไม่จำเป็นต้องเข้าแถวชำระค่าสินค้าก่อนออกจากร้านของ Amazon หรือ ระบบบัญชีการเงินที่สามารถออกเอกสารซื้อขายให้กับสองพันกว่าเจ้าหนี้แบบอัตโนมัติต่อวัน พัฒนาการของเทคโนโลยีระบบอัตโนมัติซึ่งนับรวมตั้งแต่กระบวนการทำงานอัตโนมัติโดยหุ่นยนต์ (Robotic Process Automation: RPA) จนถึงเทคโนโลยีปัญญาประดิษฐ์ได้แปลงรูปแบบธุรกิจไปอย่างถาวร ด้วยประสิทธิภาพที่เพิ่มขึ้น เพิ่มประสิทธิผล สร้างผลกำไร ก่อให้เกิดประสบการณ์ใหม่ๆ ให้กับลูกค้า คาดว่าจะมีการลงทุนจำนวนมหาศาลกับเทคโนโลยีระบบอัตโนมัตินี้ บทวิเคราะห์จาก Capgemini Research Institute คาดการณ์ว่าตลาดระบบปัญญาประดิษฐ์สำหรับงานสำนักงาน เช่น การจัดการทั่วไป การจำหน่าย การบริการมืออาชีพ และการบริหาร จะมีขนาดการเติบโตสูงถึง 48.5 พันล้านเหรียญสหรัฐในปี 2021 เพราะต่างก็เชื่อว่าการลงทุนกับเทคโนโลยีดังกล่าวนำไปสู่ผลลัพธ์ที่คุ้มค่าอย่างแน่นอน
WHAT IS ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION?
กระบวนการอัตโนมัติโดยหุ่นยนต์ (Robotic Process Automation: RPA) คือ การใช้หุ่นยนต์ที่ควบคุมด้วยซอฟต์แวร์ที่มีความสามารถเชิงปัญญาทำงานที่เดิม มีเพียงแต่มนุษย์ที่ทำได้เท่านั้นในอดีต ระบบอัตโนมัติส่งผลต่อความคล่องตัวในบริหารจัดการกิจกรรมทางธุรกิจต่างๆ ทั้งนี้ KPMGG วิเคราะห์และแบ่งระบบอัตโนมัติออกเป็น 3 คลาสด้วยกัน ได้แก่ ระบบอัตโนมัติพื้นฐาน ระบบอัตโนมัติแบบก้าวหน้าและระบบอัตโนมัติแบบระลึกรู้ โดยที่ระบบอัตโนมัติพื้นฐาน หมายถึง ระบบที่แทนที่กิจกรรมกระบวนการทางธุรกิจที่อาศัยใช้แรงงานมนุษย์ เช่น งานสั่งซื้อสินค้า งานส่งเคลม และงานใบกำกับภาษี

Source: Robotic Process Automation (PricewaterhouseCoopers)
ระบบอัตโนมัติแบบก้าวหน้าสามารถรับมือกับข้อมูลที่มีลักษณะไม่เป็นโครงสร้างได้ ทั้งนี้ เพราะว่ามีฐานความรู้ฝังอยู่ในตัวระบบ ตัวอย่างของการประยุกต์ใช้ระบบฯ ได้แก่ งานสนับสนุนทางไอที งานสั่งซื้อสินค้า และงานดูแลกระบวนการเคลม ส่วนระบบอัตโนมัติแบบระลึกรู้มีความซับซ้อนและก้าวหน้ามากซึ่งจะประกอบไปด้วยเทคโนโลยี Machine Learning ปัญญาประดิษฐ์ การประมวลผลภาษาธรรมชาติ และการวิเคราะห์ด้วยศาสตร์แห่งข้อมูล สิ่งเหล่านี้นับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเกิดใหม่ มาพร้อมความสามารถในการคิดประมวลผล การเรียนรู้ ที่คล้ายคลึงกับมนุษย์ ซึ่งออกแบบมาเพื่อให้มีความสามารถในการศึกษาหาคำตอบให้กับปัญหาด้วยตัวเองและบูรณาการความรู้เดิมเพื่อสร้างนวัตกรรม มักใช้ในงานจำพวก Self-Services ให้ลูกค้าสามารถจัดปัญหาผ่านระบบฯ ด้วยตัวเองได้ และงานอื่นที่มีความซับซ้อนและไม่ชัดเจน
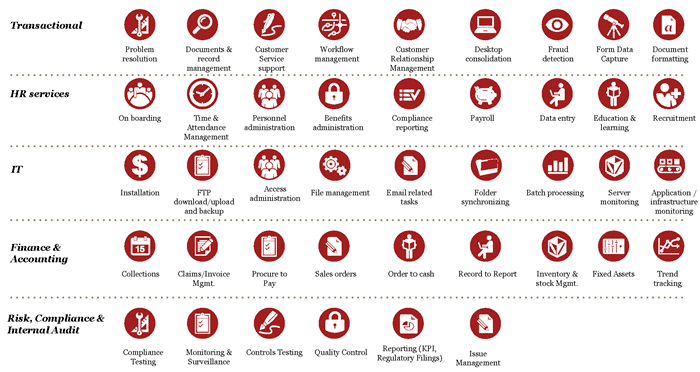
Source: Robotic Process Automation (PricewaterhouseCoopers)
RPA DEPLOYMENT FOR VALUE
โดยปัจจัยหลักที่องค์กรภาคธุรกิจจำเป็นจะต้องดำเนินการให้เสร็จสิ้นก่อนการนำระบบออโตเมชันมาใช้บงานจริง จากบทวิเคราะห์ของ Deloitte ได้กล่าวถึงปัจจัยทั้ง 3 ประกอบด้วย ประการแรกจะต้องกำหนดวิสัยทัศน์และกลยุทธ์ให้ชัดเจนเสียก่อน ในขั้นตอนนี้ผู้บริหารจะต้องทบทวนสถานภาพทางด้านเทคโนโลยีขององค์กรให้เข้าใจอย่างถ่องแท้ว่าเทคโนโลยีใดที่ควรนำมาใช้ ด้วยผลอะไร ซึ่งอาจเริ่มด้วยการนำระบบอัตโนมัติมาใช้เพียงระบบเดียวก่อนหรือว่าจะนำมาใช้กับทุกกระบวนการทั้งองค์กร องค์กรสามารถบรรลุขั้นตอนที่กล่าวมาได้ก็ต่อเมื่อสามารถระบุหรือกำหนดปัจจัยทางธุรกิจไม่ว่าจะเป็นความพร้อมขององค์กร ศักยภาพในการนำมาประยุกต์ใช้ และทำอย่างไรจึงจะได้เห็นผลที่ชัดเจนอย่างรวดเร็วและยั่งยืน
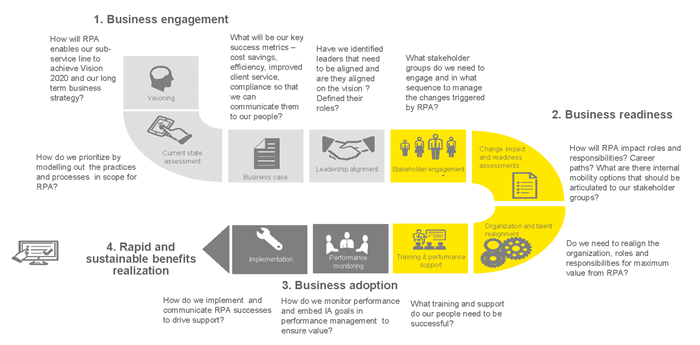
Source: Automation for the Intelligence Enterprise (Ernst & Young)
ประการที่สองบริษัทจำเป็นจะต้องสร้างโครงสร้างพื้นฐานที่รองรับศักยภาพของระบบออโตเมชันที่กำลังจะนำมาใช้งานขั้นตอนนี้จำเป็นต้องติดตั้งใช้งาน การบำรุงรักษา และลดความเสี่ยงที่จะเกิดขึ้นจากการติดตั้งใช้ สิ่งที่จะขาดไม่ได้เลยก็คือองค์กรต้องมีกรอบงานบริหารจัดการมารองรับเพราะระบบออโตเมชันมิได้ตั้งอยู่บนสุญญากาศ กรอบงานดังกล่าวนี้จะต้องมีทิศทางที่สอดคล้องกับมาตรฐานและการปฏิบัติงาน ประการที่สามประการสุดท้าย องค์กรควรมีโมเดลของการบำรุงรักษาและคงไว้ของระบบฯ โดยรวมแล้วความสำเร็จในการบำรุงรักษาระบบนั้นเป็นผลพวงมาจากปฏิสัมพันธ์ระหว่างบุคลากรกระบวนการทางธุรกิจและเทคโนโลยี
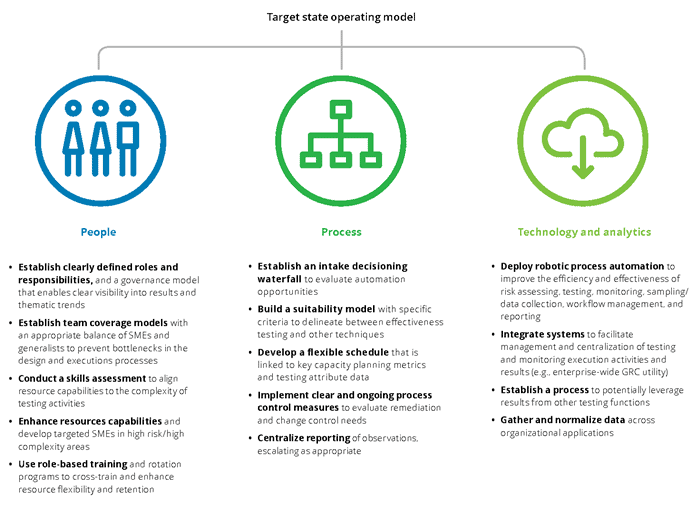
Source: Adopting Automation in Internal Audit (Deloitte)
TAKE-HOME MESSAGE
ดังนั้น ก่อนที่ติดตั้งใช้งาน RPA จะต้องสร้างกลยุทธ์ระยะยาวในขณะที่สามารถขับเคลื่อนให้เกิดประโยชน์กับองค์กรในระยะกลาง เพราะในระยะสั้นคงยากที่มองเห็นผลกระทบด้านบวก เพื่อให้เห็นผลความสำเร็จของระบบออโตเมชัน อาจเริ่มต้นจากการทดลองนำระบบดังกล่าวมาใช้ในแค่บางกระบวนการเสียก่อน เมื่อสำเร็จแล้วจึงนำระบบออโตเมชันไปใช้กับส่วนงานอื่นๆ เมื่อฟังดูแล้วอาจดูเหมือนว่าการนำระบบอัตโนมัติมาใช้ในกระบวนการทุกงานก็คงจะดี แต่อย่างไรก็ตาม ระบบดังกล่าวนี้เหมาะสมกับเพียงกระบวนการหรือเพียงบางงานเท่านั้น และแม้คุณประโยชน์ของระบบอัตโนมัติจะมีอยู่มหาศาลก็จริง ขอให้คิดว่า RPA เป็นระบบที่ขีดความสามารถ และประโยชน์ที่จะเกิดขึ้นจะมาจากการพัฒนาระบบ ไม่ใช่มาจากตัวระบบเพียงลำพัง