Asst. Prof. Suwan Juntiwasarakij, Ph.D., MEGA Tech Senior Editor
จักรกล คอมพิวเตอร์ และหุ่นยนต์ ก้าวหน้าไปมากจนทำงานแทนมนุษย์ได้ มนุษย์เราสามารถแก้ไขปัญหา ปฏิบัติภารกิจที่ไม่มีแบบแผน มีความคิดสติปัญญาที่จะวิเคราะห์ สร้างสรรค์ และตัดสินใจได้ และเนื่องมาจากเทคโนโลยีปัญญาประดิษฐ์ การเรียนรู้ของเครื่องจักร และหุ่นยนต์ ทำให้เครื่องคอมพิวเตอร์และจักรกลสามารถทำงานได้ดีกว่ามนุษย์ ด้วยความผิดพลาดที่น้อยกว่า สามารถทำงานต่อเนื่องได้โดยไม่หยุดพักผ่อน อีกทั้ง ยังมีประสิทธิภาพสูง อย่างไรก็ดี จักรกลที่ว่านี้ก็ยังมีปัญหากับงานที่ต้องใช้สติปัญญา ไม่มีแบบแผนรองรับ งานที่ระบบอัตโนมัติไม่สามารถทำได้
Redefining work by human capabilities
The Human Work of The Future
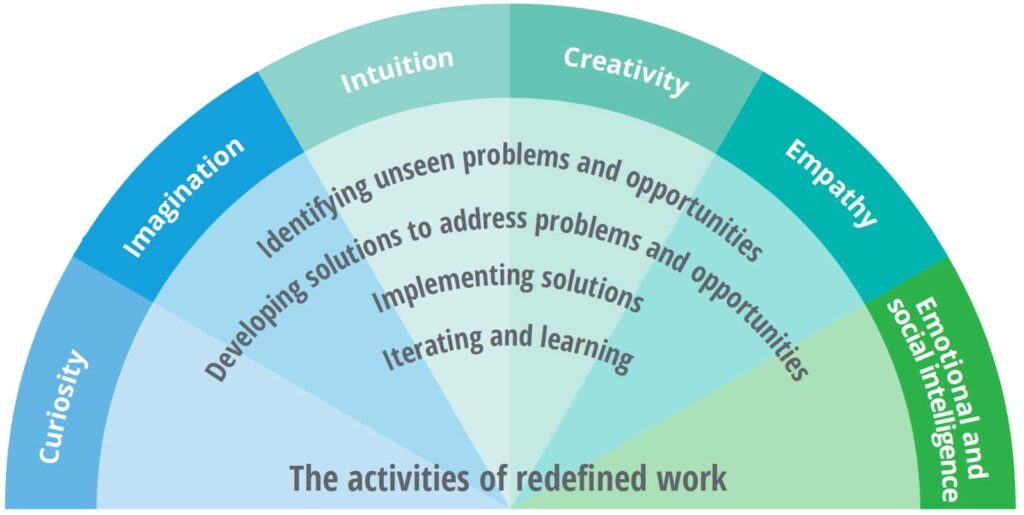
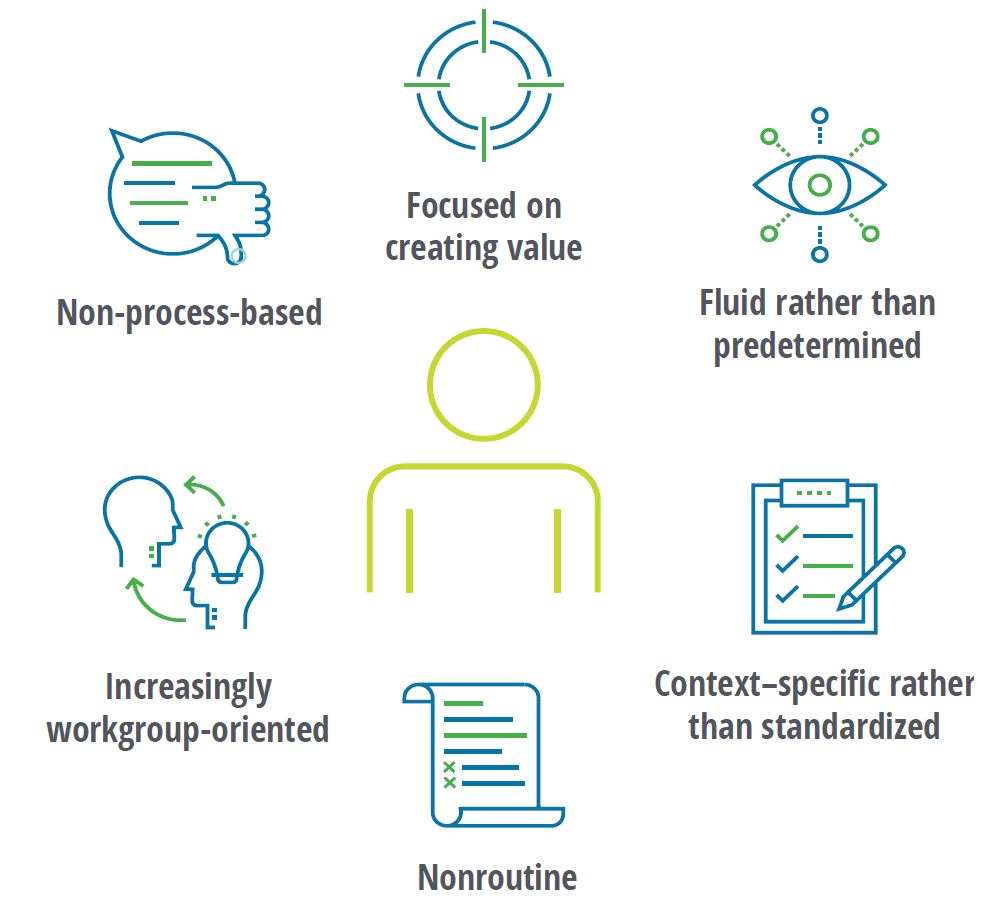
เครื่องจักรที่มีความสามารถในการประมวลผลเหล่านี้ทำให้มนุษย์ในวันนี้ได้มีโอกาสทบทวนนิยามความหมายของ “งาน” การพัฒนาทักษะแรงงานใหม่หรือนำเทคโนโลยีใหม่มาใช้ในการทำงานเดิมนั้นไม่ใช่วิถีทางการรับมือสถานการณ์แรงงานที่เกิดประโยชน์แก่องค์กรแต่อย่างใด มีแต่เพียงการทบทวนความหมายและโครงสร้าง “งาน” เท่านั้นที่สร้างคุณค่าให้แก่องค์กร ลูกค้า และแรงงาน และมีเพียงแต่มนุษย์ที่มีสัญชาตญาณเท่านั้นที่จะทำงานมีความหมายที่ต่างจากเดิม ผู้เขียนจึงขอนำเสนอวิสัยทัศน์แห่งอนาคตของ DHL ซึ่งเป็นตัวอย่างของความพยามที่จะผสานการทำงานร่วมกันระหว่างมนุษย์และเครื่องจักรกล
Source: Silence the noise, Deloitte Review, January 2019
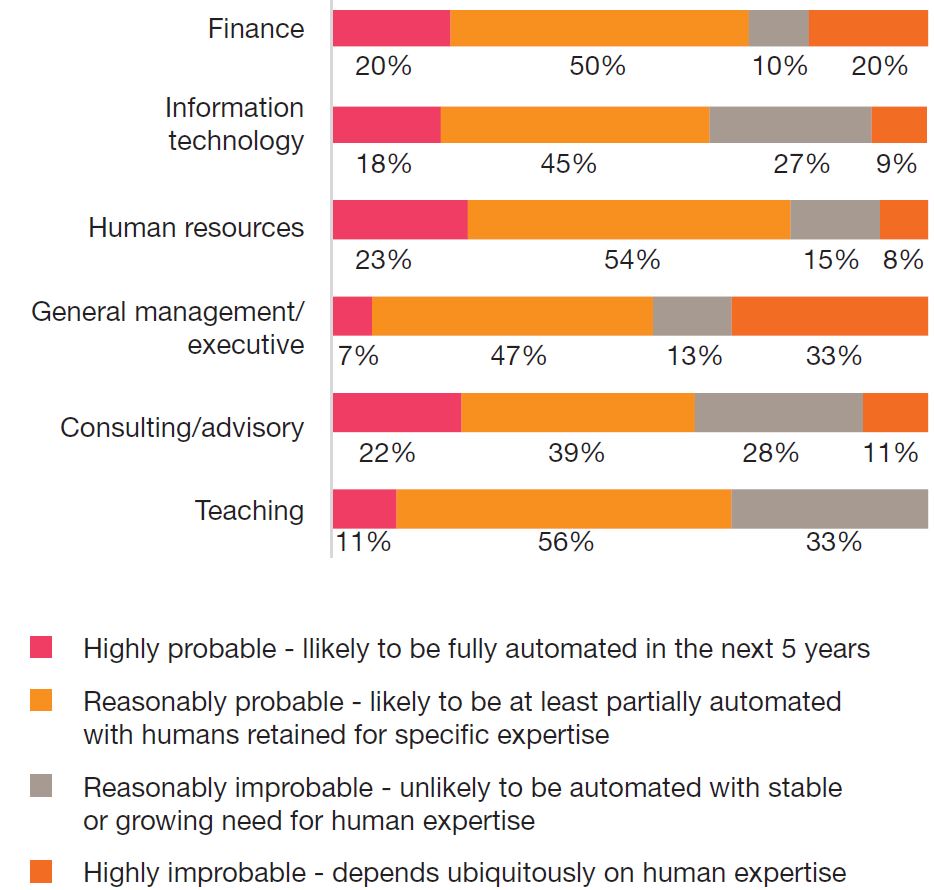
Source: How AI is reshaping jobs in India, PWC
Human-Machine Collaboration
เพื่อที่จะแสดงให้เห็นว่ามนุษย์และเครื่องจักรกลสามารถทำงานร่วมกันได้ British Transportation Research Library บริษัท DHL และบริษัทผลิตรถบรรทุก DAF ได้ร่วมโครงการกันเพื่อสร้างระบบบริหารจัดการเส้นทางให้แก่บรรทุกบนสายมอเตอร์เวย์ของสหราชอาณาจักร เทคโนโลยีการสื่อสารภายในกลุ่มยานพาหนะขนาดย่อย และระบบนำร่องการขับขี่ทำให้รถบรรทุกสามารถขับเคลื่อนไปอย่างอัตโนมัติ โดยประสานจังหวะความเร็วอัตราเร่ง การหมุนของพวงมาลัยในทิศทางเดียวกัน การชะลอความเร็ว และทิ้งระยะห่างอย่างเหมาะสม
อย่างไรก็ดี ระบบดังกล่าวนี้ควบคุมด้วยมนุษย์ผู้ขับขี่นำขบวนและที่พร้อมอยู่หลังพวงมาลัยบนรถบรรทุกคนอื่นๆ อีกจำนวนหนึ่ง และในที่สุดระบบดังกล่าวนี้จะเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบจัดการ Supply-Chain ครบวงจรจากต้นทางจนถึงลูกค้าปลายทาง สัญญาณเบื้องต้นที่บ่งบอกถึงการเปลี่ยนแปลงเหล่านี้ได้จากการจัดการภายในคลังสินค้า การจัดเส้นทางรถบรรทุกระยะทางไกล การส่งมอบสินค้าปลายทาง ซึ่ง DHL ได้ศึกษาสำรวจและทดสอบการประยุกต์ใช้เทคโนโลยีหุ่นยนต์ที่มีความสามารถในการประมวลผลและเทคโนโลยีอัตโนมัติ จึงทำให้เกิดแนวคิดการออกแบบศูนย์กจำหน่ายและกระจายสินค้า ศูนย์สรรหาและจัดเตรียมสินค้า และการส่งมอบสินค้าถึงมือลูกค้าปลายทาง ดังที่จะนำเสนอดังต่อไปนี้
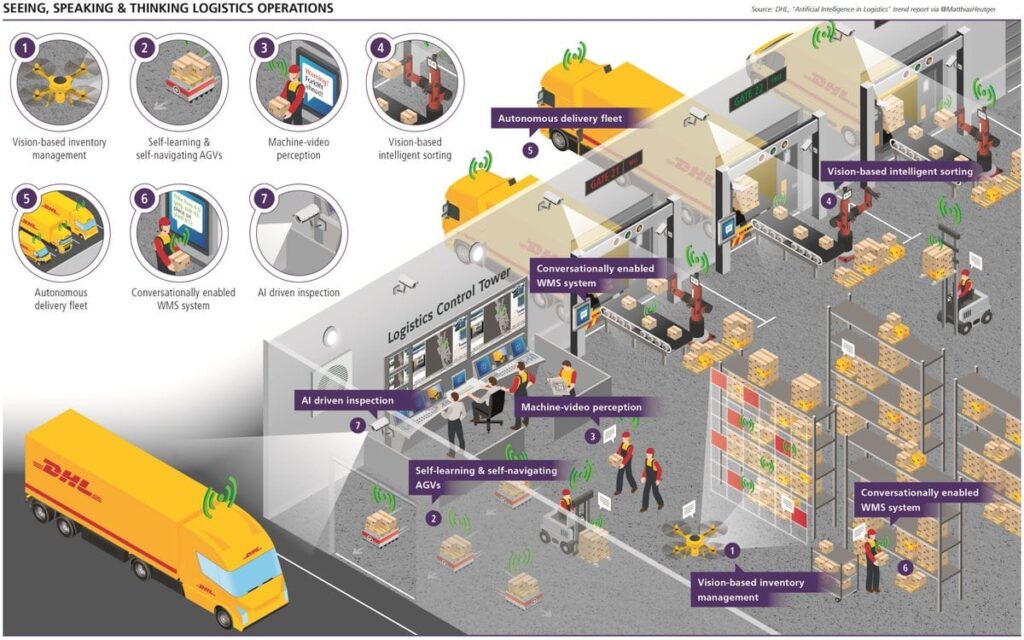
Source: Siemens
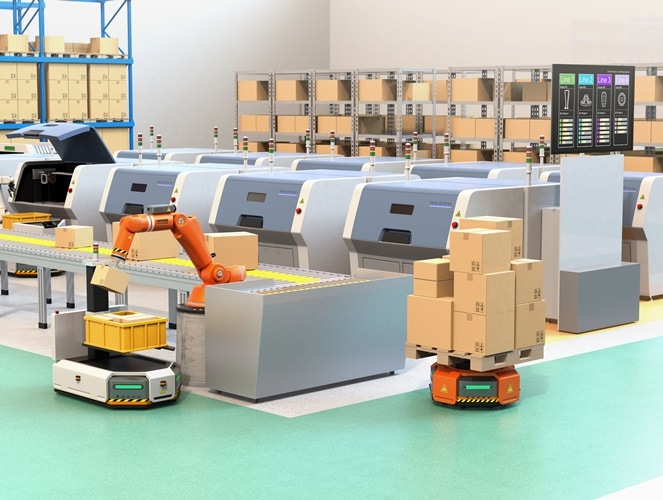
DHL Future Vision: Distribution Centers
มนุษย์สามารถสอนหุ่นยนต์ให้ทำงานที่ไม่ซับซ้อนและงานที่ซ้ำซ้อนได้ หรือไม่ก็หุ่นยนต์ต่อเชื่อมเข้าสู่คลาวด์และดาว์นโหลดความรู้ที่จำเป็นต่อการทำงานมาใส่ตัวเองโดยอัตโนมัติ มนุษย์จึงขยับขึ้นไปทำงานที่ต้องใช้ความรับผิดชอบ ท้าทายกว่า และอาศัยทักษะ เช่น การบริหารจัดการ การติดต่อประสานการทำงาน การซ่อมแซมหุ่นยนต์ และงานอื่นที่มีความซับซ้อนไม่สามารถแก้ไขปัญหาด้วยวิธีการธรรมดาได้ ความน่าเชื่อถือต่อระบบการทำงานจึงเพิ่มมากขึ้นไปด้วยเนื่องจากอัตราการเกิด “Single Point of Failure” ลดลงในแต่ละศูนย์ และหากเกิดความเสียหายขึ้นในกระบวนการใดการบวนการหนึ่ง สิ่งต้องทำก็เพียงแค่ทดแทนเครื่องจักรกลที่เสียหายด้วยจักรกลชิ้นใหม่ กระบวนการงานที่จะเดินต่อเนื่องได้ทันที
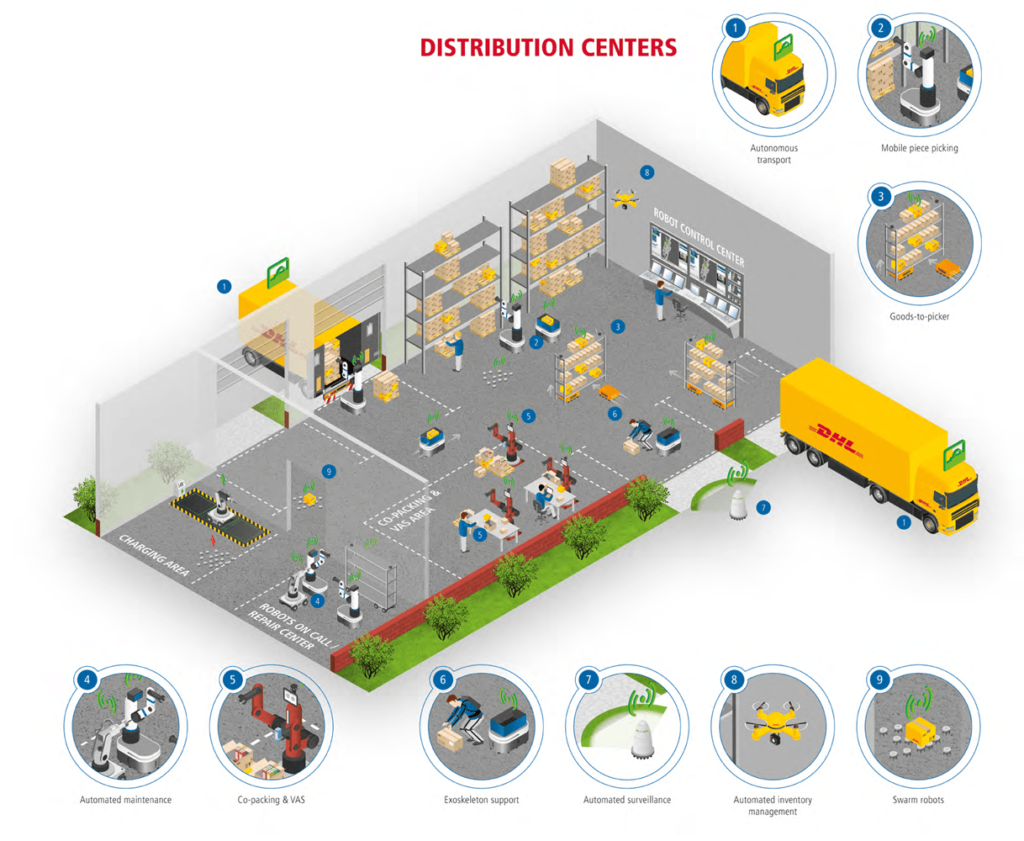
Source: Siemens
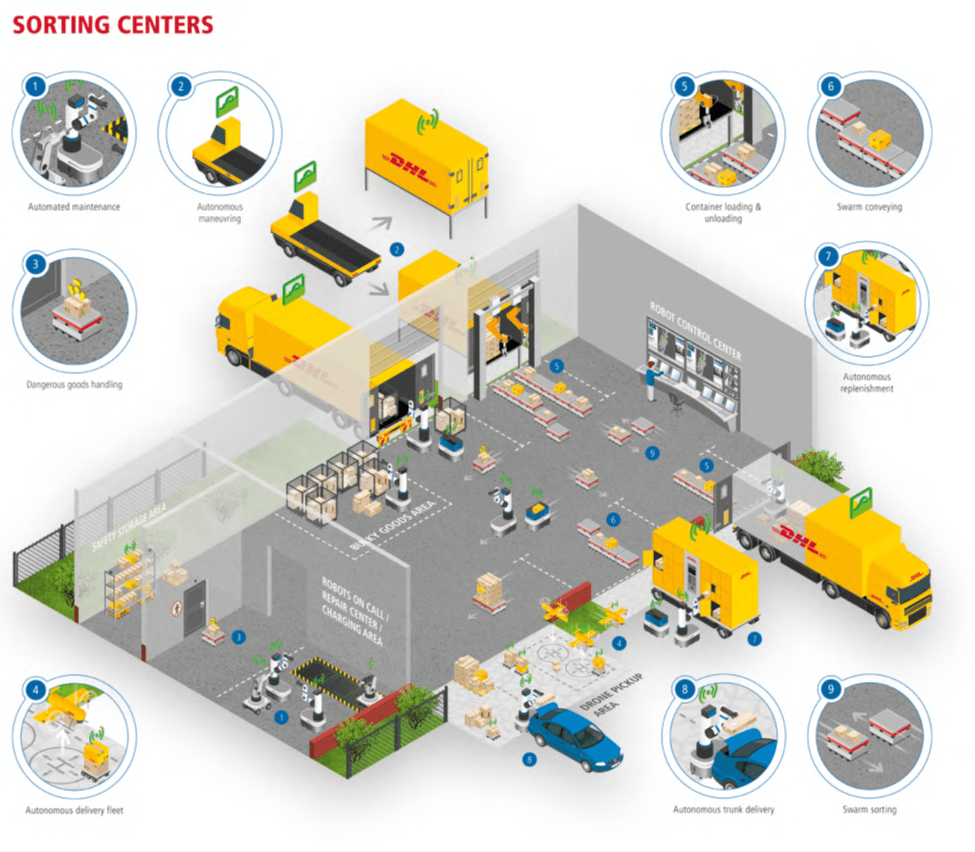
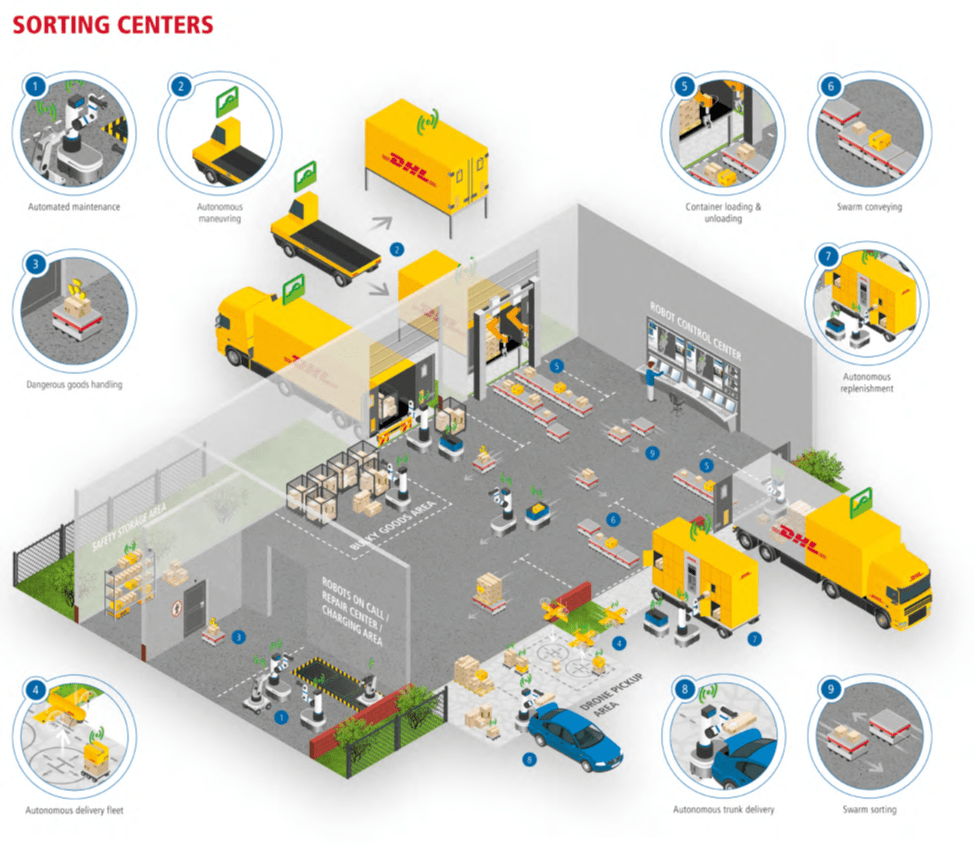
DHL Future Vision: Sorting Centers
แม้ว่าจะเป็นกะสุดท้ายของวัน คลังสินค้าระบบหุ่นยนต์และศูนย์สรรหาและจัดเตรียมสินค้าก็ยังทำงานได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพเหมือนกับเป็นกะแรกของวัน รองรับสินค้าและอำนวยความสะดวกในการเตรียมการจัดส่งเพื่อให้สินค้าได้ส่งถึงมือลูกค้า ด้วยลักษณะการทำงานที่เป็นระลอกรองรับสินค้าอย่างไม่ขาดสายนี้ เป็นการใช้ประโยชน์จากอุปกรณ์เครื่องมือได้อย่างเต็มที่ สินค้าหมุนเวียนเร็ว ต้นทุนค่าใช้จ่ายเพื่อจัดเก็บสินค้าจึงลดลงตามไปด้วย การให้บริการจึงมีความรวดเร็วคล่องตัว เริ่มจากสินค้าจะเข้ามาสู่ศูนย์สรรหาและจัดเตรียมสินค้า รถบรรรทุกขนสินค่าเป็นแบบขับเคลื่อนด้วยตัวเอง ตามตารางเวลาที่กำหนดไว้ โดยที่ทิศทางการเดินรถและการเคลื่อนที่นั้นถูกกำหนดด้วย GPD และระบบบริหารจัดการรถบรรทุกไร้คนขับ เมื่อรถบรรทุกได้เทียบท่าที่ศูนย์สรรหาและจัดเตรียมสินค้า ขั้นตอนที่เกิดขึ้นคือบรรจุสินค้าลงสู่รถบรรทุกด้วยแขนกล และเป้าหมายถัดไปของรถบรรทุกคนนี้อาจจะเป็นศูนย์สรรหาและจัดเตรียมสินค้าอื่นที่อยู่ในเครือข่าย หรืออาจเป็นการส่งมอบสินค้าถึงมือลูกค้าปลายทางก็ได้ อย่างไรก็ดี พัสดุที่ผู้รับอยู่ในพื้นที่ยากต่อการเข้าถึง ก็อาจมีความจำเป็นต้องใช้โดรนก็สามารถทำได้
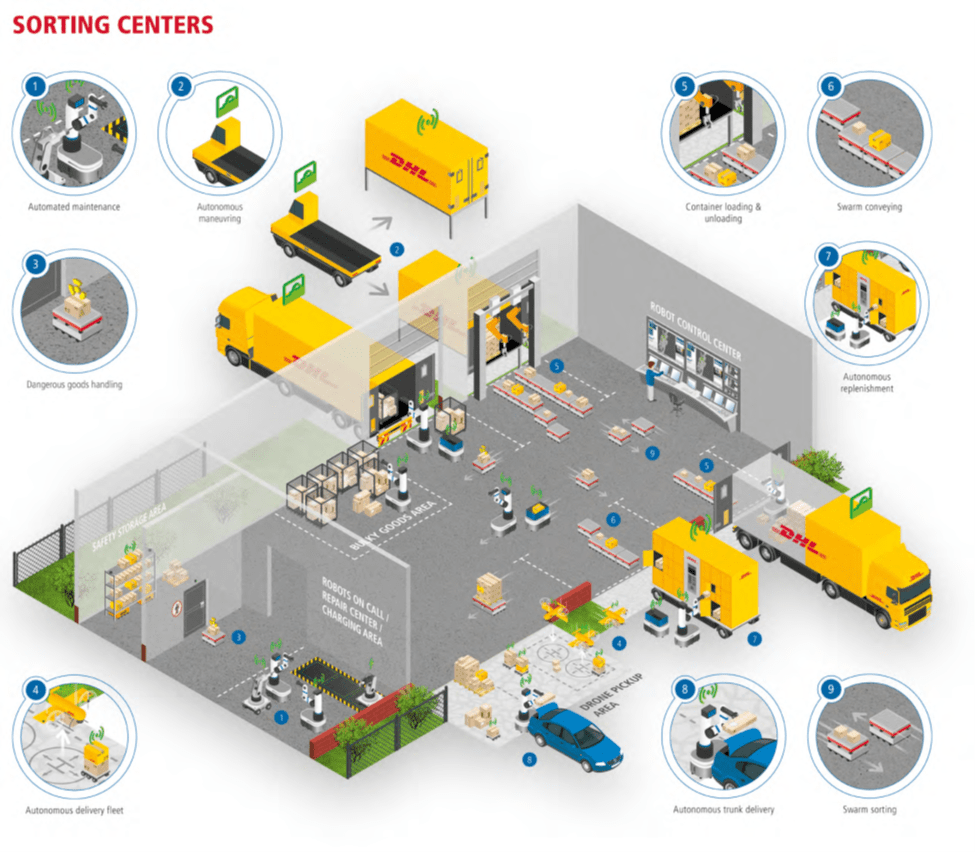
Source: Robotics in Logistics, DHL Trend Research
DHL Future Vision: Last-Mile Delivery
ในอนาคตมนุษย์จะมีปฏิสัมพันธ์กับหุ่นยนต์จนเป็นเรื่องปกติ ที่จริงหุ่นยนต์ที่ทำหน้าที่ส่งมอบสินค้านั้นมีความปลอดภัยสูงเนื่องจากมีระบบป้องกันการชน ที่ประกอบด้วยอุปกรณ์เซ็นเซอร์ที่ทันสมัย เช่น กล้อง ระบบสแกนด้วยเลเซอร์ และเซนเซอร์ตรวจวัดระยะทาง ยิ่งผสานการทำงานเข้ากับระบบคลาวด์ หุ่นยนต์เหล่านี้ก็จะมีขีดความสามารถให้บริการที่มีคุณภาพกับลูกค้ามากขึ้นไปด้วย เช่นหุ่นยนต์จะสามารถสื่อสารกับลูกค้าได้หลายภาษา เข้าใจถึงภาวะอารมณ์ของลูกค้า เข้าใจพฤติกรรมลูกค้าโดยอาศัยข้อมูลที่เกี่ยวกับลูกค้าที่มีอยู่ และสามารถตอบโต้ได้อย่างเหมาะสม อย่างไรก็ดี สินค้าชิ้นใหญ่จะยังคงอาศัยมนุษย์เป็นผู้ส่งมอบถึงมือลูกค้า หรืออาจจะเป็นมนุษย์เป็นผู้ส่งมอบโดยที่มีหุ่นยนต์เป็นผู้ช่วยที่บรรจุสินค้าเดินตามหลังมนุษย์ก็ได้
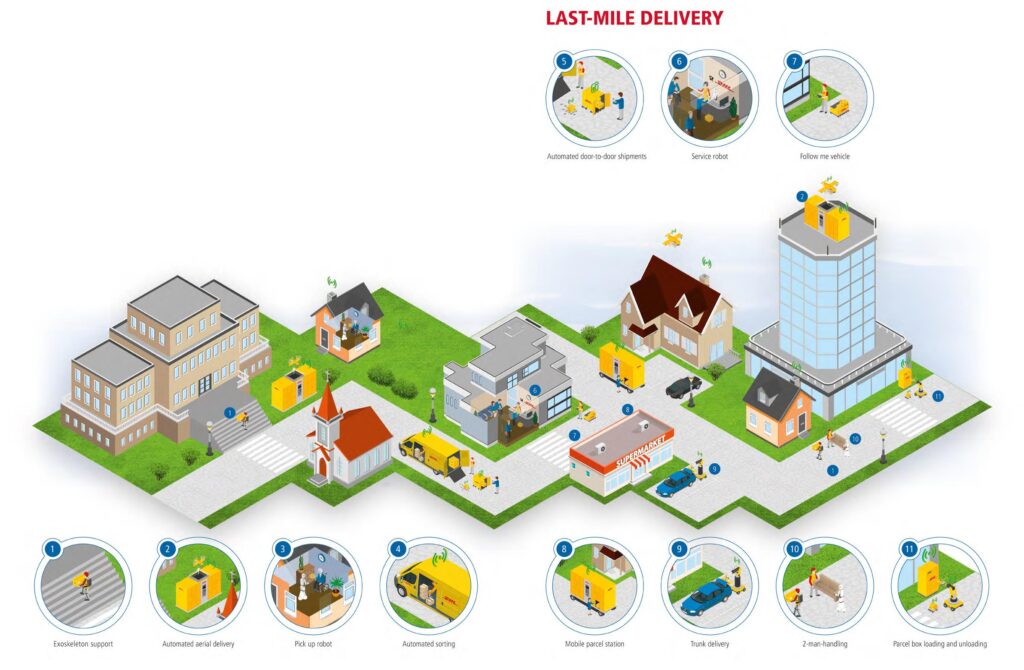
Source: Robotics in Logistics, DHL Trend Research
Take-Home Message
แม้หุ่นยนต์เข้ามาโดยกลายเป็นส่วนประกอบของโลกโลจิสติกส์ แต่จากตัวเลขจากการศึกษาวิจัยก็ยังแสดงให้เห็นว่าแรงงานทางโลจิสติกส์ประเทศเทศที่พัฒนาแล้วกำลังจะขาดแคลนอย่างหนักในอีก 20 ปีข้างหน้า ปัญหานี้เนื่องมาจากปริมาณการช้อปปิ้งออนไลน์ที่สูงขึ้นทั่วโลก ปริมาณการไหลของสินค้าจึงสูงขึ้นไปด้วย และสินค้าย่อมต้องการที่อยู่ (คลังสินค้า ) และต้องการการดูแล (แรงงาน) อนาคตของการนำหุ่นยนต์มาร่วมทำงานกับแรงงานมนุษย์ ประโยชน์ที่เกิดแก่โลกโลจิสติกส์ย่อมจะมาจากเทคโนโลยีจักรกลทรงปัญญาอันก้าวหน้า