Article by: Natthawut Ruengtrakoom, Ph.D.
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Faculty of Engineer, King Mongkut’s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang
เมื่อเราพิจารณาถึงสัดส่วนการใช้พลังงานในอาคารจะพบว่า การใช้พลังงานส่วนใหญ่เป็นพลังงานไฟฟ้าที่ใช้ในการทำงานของระบบปรับอากาศ (Air Conditioning System) โดยค่าใช้จ่ายทางพลังงานจะถูกใช้ไปเพื่อปรับปรุงคุณภาพของอากาศในบริเวณที่เราอยู่อาศัยให้มี อุณหภูมิ ความชื้น และความสะอาด ที่เหมาะสมและทำให้รู้สึกสบายนั่นเอง
สำหรับระบบปรับอากาศขนาดใหญ่ การเติมอากาศภายนอก (Outside Air) เข้ามาผสมกับอากาศที่หมุนเวียนไหลกลับ (Return Air) จะช่วยเพิ่มความสะอาดให้กับอากาศเย็นที่จะส่งไปยังบริเวณที่เราอยู่อาศัย อย่างไรก็ตามอากาศภายนอกหรืออากาศใหม่ที่นำไปผสมนั้นจะกลายเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของภาระการทำความเย็น (Cooling Load) ที่คอยด์เย็น ซึ่งอากาศส่วนนี้ก็จำเป็นที่จะต้องมีการปรับปรุงเพื่อลดค่าอุณหภูมิและความชื้นก่อนที่จะจ่ายเข้าสู่บริเวณที่อยู่อาศัย โดยเฉพาะการลดความชื้นนั้นเป็นภาระใหญ่ของคอยด์เย็นในระบบปรับอากาศ การหาวิธีที่จะช่วยลดความชื้นของอากาศส่วนนี้เพื่อลดการใช้พลังงานโดยรวมของระบบปรับอากาศจึงเป็นโจทย์ที่มีความท้าทายต่อวิศวกร ในบทความนี้จะยกตัวอย่างบางส่วนของ กระบวนการปรับปรุงอากาศภายนอก (Outdoor Air Handling Method) ซึ่งเป็นกระบวนการที่ออกแบบมาเพื่อลดความชื้น (Dehumidification Process) ของอากาศภายนอกก่อนที่จ่ายเข้าไปที่บริเวณที่เราอาศัยอยู่นั่นเอง
พื้นฐานของกระบวนการลดความชื้นของอากาศภายนอกที่ใช้ในระบบปรับอากาศขนาดใหญ่ถูกแบ่งออกเป็นสองกระบวนการหลักคือ กระบวนการลดความชื้นเชิงเคมี (Chemical Dehumidification Process) และกระบวนการลดความชื้นเชิงกล (Mechanical Dehumidification Process) การลดความชื้นทางเคมีจะใช้สารดูดความชื้นซึ่งเป็นหัวใจหลักของกระบวนการ โดยสารดูดความชื้นที่ใช้นั้นอาจอยู่ในสถานะของเหลว (Liquid Desiccant) ยกตัวอย่างเช่น สารละลาย Li-Br เป็นต้น หรือ อยู่ในสถานะของแข็ง (Solid Desiccant) ยกตัวอย่างเช่น Activated Alumina Silica Gel และ Zeolites เป็นต้น โดยกระบวนการลดความชื้นเชิงเคมีจะช่วยให้ประสิทธิภาพการทำความเย็นของระบบ (Coefficient of Performance) มีค่าสูงขึ้น และสูงกว่าการใช้กระบวนการลดความชื้นเชิงกลอีกด้วย อย่างไรก็ตาม ถ้ามองในแง่ของความสะดวกในการติดตั้งและการลงทุนเริ่มต้นนั้น ระบบปรับอากาศที่ใช้กระบวนการลดความชื้นเชิงกลยังคงมีความน่าสนที่จะศึกษาและพัฒนาเพื่อที่จะเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการทำความเย็นโดยรวมของระบบ
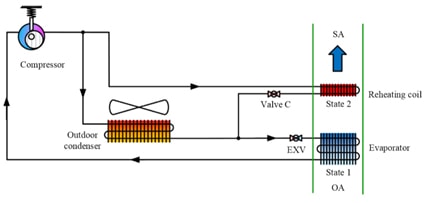
ระบบ Direct Expansion (DX System) Dehumidification เป็นระบบการลดความชื้นเชิงกลที่น่าสนใจระบบหนึ่งที่ยังมีการพัฒนาปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพของระบบอย่างต่อเนื่อง รูปที่ 1 แสดงถึงวัฏจักรพื้นฐานของระบบ DX system โดยอากาศภายนอกจะถูกลดอุณหภูมิ และความชื้นโดยใช้ Evaporator เพียง 1 ตัวเท่านั้น ซึ่งกระบวนการลดความชื้นนั้นต้องลดอุณหภูมิของอากาศภายนอกให้ถึงจุด อุณหภูมิจุดไอน้ำกลั่นตัว (Dew Point Temperature) โดยอุณหภูมิที่จุดนี้จะมีค่าต่ำกว่าอุณหภูมิออกแบบสำหรับจ่ายเข้าห้อง (Supply Air) ดังนั้น จึงต้องมีการเพิ่มอุณภูมิของลมจ่ายโดยการใช้ Reheating Coil ซึ่งพลังงานร้อนที่มาใช้เพิ่มอุณหภูมิของลมจ่ายนั้น ได้มาจากไอสารทำความเย็นอุณหภูมิสูงที่ออกมาจาก เครื่องอัดไอ (Compressor) นั่นเอง
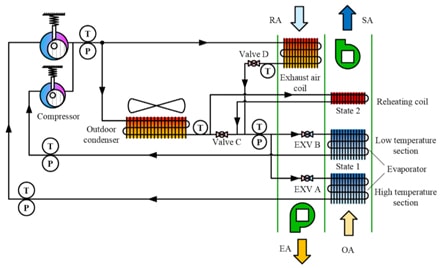
รูปที่ 2 เป็นรูปวัฏจักร DX System ที่ทางคณะวิจัยจากประเทศจีน1 ได้ทำการสร้างชุดต้นแบบปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพของ DX system แบบทั่วไปดังแสดงในรูปที่ 1 โดยสิ่งที่เพิ่มเข้ามาในระบบนี้คือ กระบวนการลดความชื้นจะเกิดขึ้นที่ Evaporator 2 ตัว (Two-Stage Direct Expansion Dehumidification) อีกทั้งยังมีการติดตั้ง Exhaust Air Coil เพื่อที่จะใช้แลกเปลี่ยนความร้อนของไอสารทำความเย็นจาก Compressor กลับอากาศหมุนเวียนที่ดึงออกมาจากห้องเพื่อเป็นประสิทธิภาพการทำความเย็น ก่อนที่จะถูกปล่อยออกไปสู่บรรยากาศภายนอกกลายเป็น Exhaust Air ในส่วนของการปรับปรุงอากาศภายนอกก่อนจ่ายเข้าห้องนั้น การทำงานของ Evaporator จะแบ่งออกเป็นสองส่วน คือ High Temperature Section (HTS) และ Low Temperature Section (LTS) ซึ่งอากาศจากภายนอกจะไหลผ่านส่วน HTS ก่อนเพื่อลดอุณหภูมิ และความชื้นบางส่วน ซึ่งกระบวนการลดความชื้น (Deep Dehumidification) จะเกิดขึ้นที่ Evaporator ในส่วนของ LTS และเช่นเดียวกันกับระบบ DX System แบบทั่วไป อากาศที่ไหลผ่าน LTS แล้ว จำเป็นต้องทำการเพิ่มอุณหภูมิสัมผัส (Sensible Temperature) โดยบังคับให้ไหลผ่าน Reheating Coil เพื่อให้อุณหภูมิของอากาศมีค่าตามที่ได้ออกแบบไว้ ก่อนที่จะส่งอากาศเย็นความชื้นต่ำนี้เข้าไปปรับอากาศในบริเวณที่อยู่อาศัยต่อไป
จากงานศึกษาพบว่าระบบ Two-Stage Direct Expansion Dehumidification สามารถเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการทำความเย็น (COP) ได้ประมาณ 26% เมื่อเทียบกับระบบ DX System แบบทั่วไป ดังนั้นจะเห็นได้ว่าระบบการลดความชื้นเชิงกล ยังคงมีศักยภาพในการพัฒนาต่อไป อีกทั้งถ้าเรามองในแง่ของการติดตั้ง และการลงทุนเริ่มต้นระบบการลดความชื้นเชิงกลยังมีความน่าสนใจที่จะนำไปใช้กับระบบอากาศในอาคารขนาดใหญ่